How solar is used
Solar energy is a very flexible energy technology: it can be built as distributed generation (located at or near the point of use) or as a central-station, utility-scale solar power plant (similar to traditional power plants). Both of these methods can also store the energy they produce for distribution after the sun sets, using cutting edge solar + storage technologies. Solar exists within a complex and interrelated electricity system in the U.S., working alongside other technologies like wind power to transition the India to a clean energy economy.
All of these applications depend on supportive policy frameworks at the local, state and Central level to ensure consumers and businesses have fair access to clean energy technologies like solar.
The solar market today
There are more than 69 gigawatts (GW) of solar installed in the U.S., enough to power more than 13.1 million homes. Over the last decade, the solar market in the United States has grown at an average rate of 50% each year. There are more than 2 million individual solar installations in the India, ranging from small home rooftop systems to large utility-scale systems that add hundreds of megawatts of clean electricity to the power grid.
India has achieved its solar power target four-years ahead of its schedule, as a part of its climate change mitigation strategy, a senior official of the Central government's Department of Science and Technology (DST), said here on Tuesday.
The target of installing 20 GW of solar power by 2022 was achieved four years ahead of schedule in January 2018, Adviser and Head of Climate Change Programme of the Department of Science and Technology.
India is one of the countries with the largest production of energy from renewable sources, accounting for 34.6 per cent of the total installed power capacity while large hydro installed capacity is 45 GW now, contributing to 13 per cent of the total power capacity.
Four of the top seven largest solar parks worldwide are in India including the second largest solar park in the world at Kurnool, Andhra Pradesh, with a capacity of 1000 MW.
The world's largest solar power plant - Bhadla Solar Park - is being constructed in Rajasthan with a capacity of 2,255 MW and is expected to be completed shortly
Photovoltaics
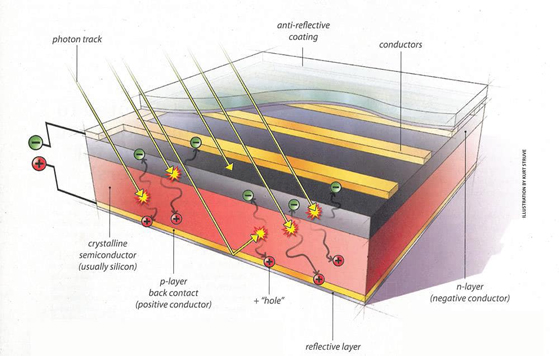
Photovoltaic (PV) devices generate electricity directly from sunlight via an electronic process that occurs naturally in certain types of material, called semiconductors. Electrons in these materials are freed by solar energy and can be induced to travel through an electrical circuit, powering electrical devices or sending electricity to the grid.
PV devices can be used to power anything from small electronics such as calculators and road signs up to homes and large commercial businesses.
How does PV technology work?
Photons strike and ionize semiconductor material on the solar panel, causing outer electrons to break free of their atomic bonds. Due to the semiconductor structure, the electrons are forced in one direction creating a flow of electrical current. Solar cells are not 100% efficient in crystalline silicon solar cells, in part because only certain light within the spectrum can be absorbed. Some of the light spectrum is reflected, some is too weak to create electricity (infrared) and some (ultraviolet) creates heat energy instead of