What is wind power?
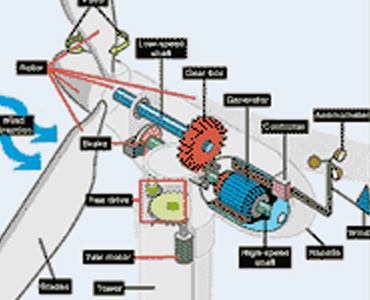
wind power (or wind power) refers to the process of creating electricity using the wind, or air flows that occur naturally in the earth’s atmosphere. Modern wind turbines are used to capture kinetic energy from the wind and generate electricity.
There are three main types of wind power:
- Utility-scale Wind: Wind turbines that range in size from 100 kilowatts to several megawatts, where the electricity is delivered to the power grid and distributed to the end user by electric utilities or power system operators.
- Distributed or "small" Wind: Single small wind turbines below 100 kilowatts that are used to directly power a home, farm or small business and are not connected to the grid.
- Offshore Wind: Wind turbines that are erected in large bodies of water, usually on the continental shelf. Offshore wind turbines are larger than land-based turbines and can generate more power.